Understanding the Different Types of Diabetes: A Comprehensive Guide
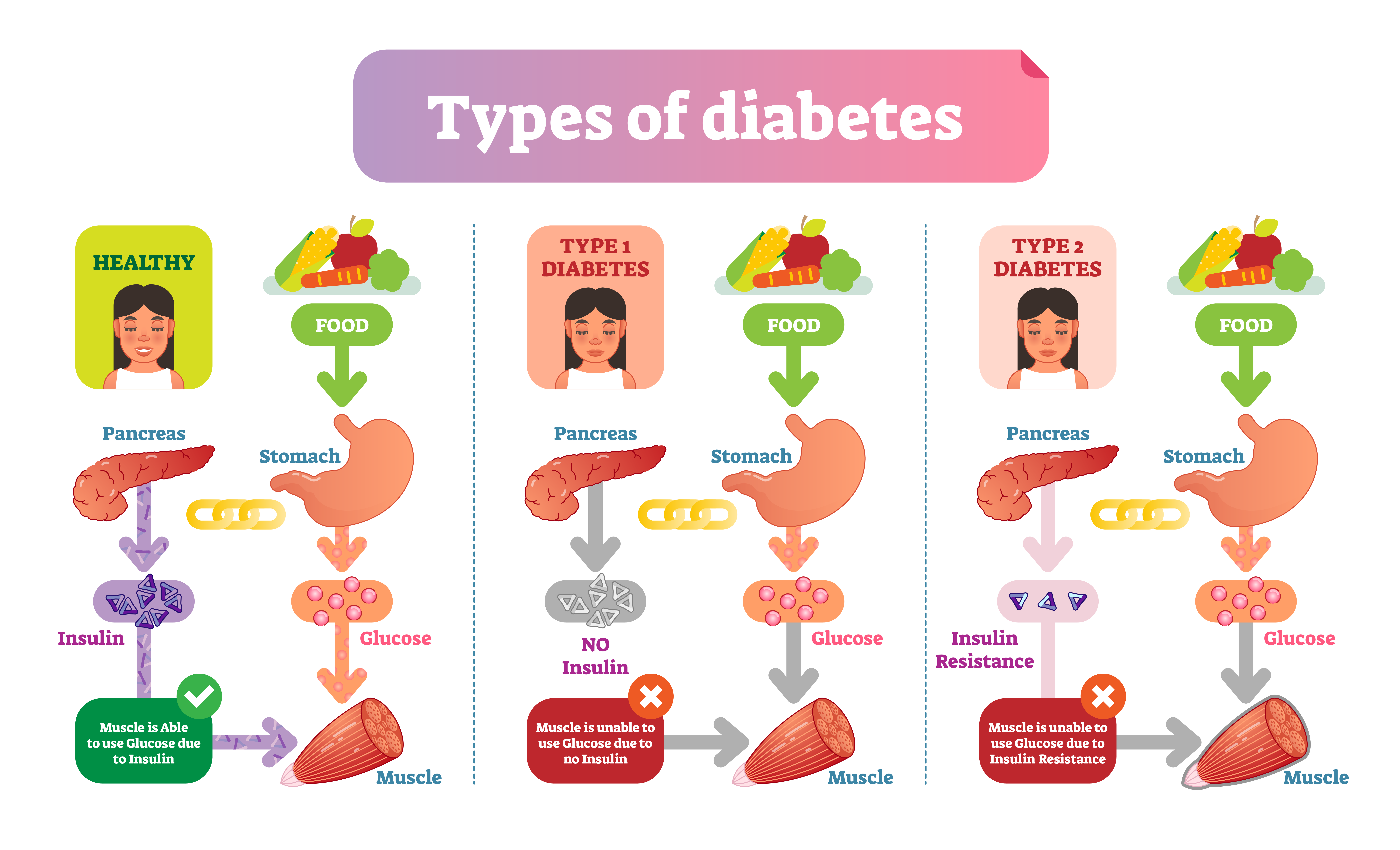
Diabetes is a chronic medical condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels. It results from either the body's inability to produce insulin (Type 1 diabetes) or inefficient use of insulin by the body (Type 2 diabetes). Here's a brief overview of the causes, symptoms, and treatments for the two main types of diabetes:
Type 1 Diabetes:
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease that typically develops during childhood or adolescence, but it can occur at any age. In this condition, the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. As a result, the body is unable to produce insulin, the hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar levels.
Causes: The exact cause of Type 1 diabetes is not entirely understood, but researchers believe that a combination of genetic and environmental factors plays a role. Family history of the disease, exposure to certain viruses, and specific genetic markers can increase the risk of developing Type 1 diabetes.
Symptoms: The symptoms of Type 1 diabetes often appear suddenly and may include:
- Excessive thirst and hunger
- Frequent urination
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue and weakness
- Blurred vision
Treatment: Managing Type 1 diabetes requires daily insulin therapy, as the body cannot produce insulin on its own. This may involve multiple daily injections or the use of an insulin pump. Additionally, regular blood sugar monitoring, a balanced diet, and regular exercise are crucial for maintaining stable blood sugar levels and overall well-being.
Type 2 Diabetes:
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes, accounting for approximately 77 million1 cases in India. Unlike Type 1 diabetes, Type 2 diabetes is characterized by insulin resistance, where the body's cells do not respond effectively to insulin, or insulin deficiency, where the pancreas does not produce enough insulin to meet the body's demands.
Causes: Type 2 diabetes is strongly associated with lifestyle factors, such as:
- Sedentary lifestyle and lack of physical activity
- Unhealthy eating habits, especially a diet high in processed and sugary foods
- Excess body weight and obesity
- Family history of diabetes
Symptoms: The symptoms of Type 2 diabetes may develop gradually and include:
- Fatigue and lethargy
- Frequent infections
- Slow-healing wounds
- Tingling or numbness in the hands and feet
- Increased hunger and thirst
Treatment: The management of Type 2 diabetes focuses on lifestyle modifications and, in some cases, medications. Lifestyle changes may include regular exercise, adopting a balanced diet, and maintaining a healthy weight. Oral medications or insulin therapy may be prescribed to improve insulin sensitivity and control blood sugar levels.
Gestational Diabetes:
Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and affects approximately 2-10%2 of pregnant women. It is characterized by high blood sugar levels that develop during pregnancy, usually around the 24th to 28th week3.
Causes: Hormonal changes during pregnancy can lead to insulin resistance, where the body's cells become less responsive to insulin, resulting in elevated blood sugar levels.
Symptoms: Gestational diabetes often does not present with noticeable symptoms. However, some women may experience:
- Excessive thirst and urination
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
Treatment: Managing gestational diabetes involves closely monitoring blood sugar levels through regular testing. Adopting a balanced diet and engaging in moderate physical activity can help control blood sugar levels. In some cases, insulin therapy may be necessary to ensure the health of both the mother and the baby.
Understanding the different types of diabetes is crucial for effectively managing the condition and improving overall health outcomes. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder that requires insulin therapy, while Type 2 diabetes is closely linked to lifestyle factors and may be managed with lifestyle changes and medications. Gestational diabetes demands special attention during pregnancy to ensure the well-being of both mother and baby.
1 Diabetes in India. Available at https://www.who.int/.
2 Prevalence of Gestational Diabetes in India by Individual Socioeconomic, Demographic, and Clinical Factors. Available at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/.
3 Gestational Diabetes and Pregnancy. Available at https://www.cdc.gov/.
